Substations
Substations control the voltage of electricity so that high-quality electricity can be carried efficiently with low loss. A total of 1,588 substations have been installed in the TEPCO service area (as of March 31, 2012), performing such operations as raising and lowering voltage and adjusting frequency.
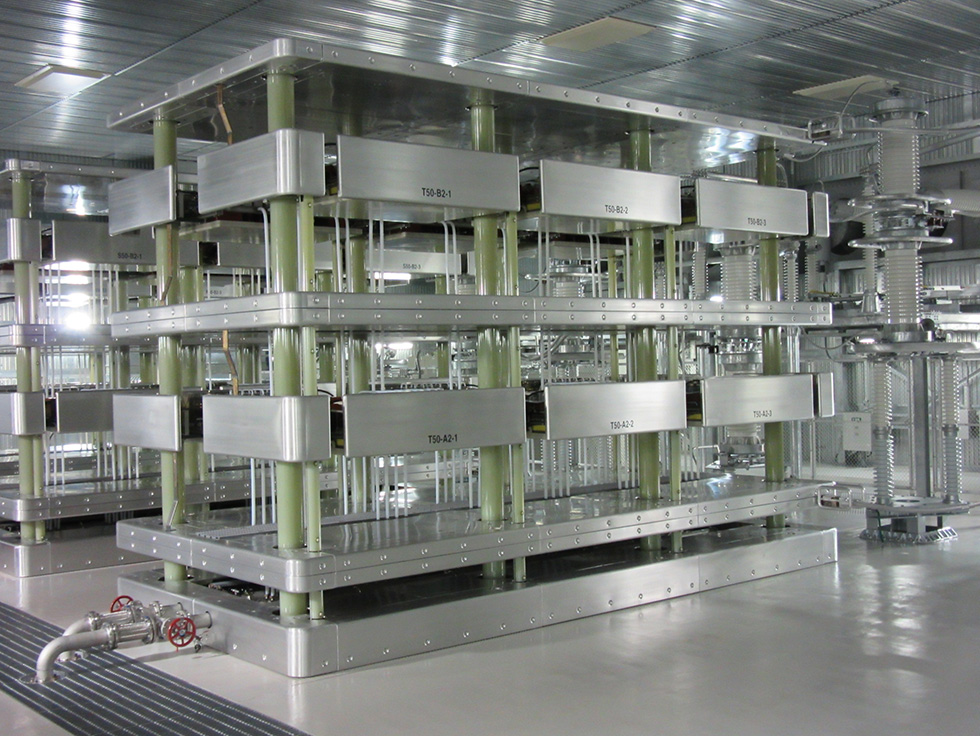

Substations Explained
High-voltage control for efficient transmission of high-quality electricity
Sending electricity at high voltages minimizes loss and allows it to be sent over thin wires. High voltages are therefore used for transmission from the power station to the vicinity of consumers, where the voltage is then lowered.
Also, by concentrating and distributing the flow of electricity, power outages can be prevented even when the flow is partially cut off due to lightning or other causes. These functions are performed by substations, which play a key role in efficient delivery of electricity.
Among the types of substations are transmission substations, including 500,000-volt substations, which have a maximum internal voltage of 500,000 volts, ultra-high-voltage substations of 275,000 volts, and primary substations of 154,000 volts. There are also 66,000-volt distribution substations for direct delivery to general customers. Each of these substations functions as a control center for adjusting the different voltages and electrical flow to ensure stable transmission.
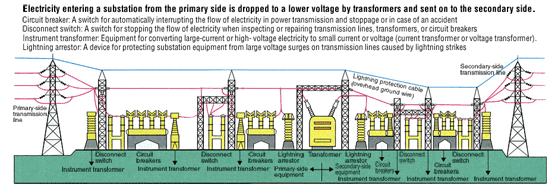
Substation Equipment
Power Interchange between East and West Japan
Electricity is supplied at 50Hz in the eastern part of Japan and at 60Hz in the west. Frequency conversion is therefore necessary when interchanging electric power between areas.
Facilities capable of performing this conversion are deployed in three locations in Japan, the Shin-Shinano Substation, Sakuma Frequency Converter Station, and Higashi-Shimizu Substation. Shin-Shinano has 600,000 kW frequency conversion equipment while the other two stations have conversion capacities of 300,000 kW each.
The types of power interchange include economical interchange for lowering the supply cost and backup interchange in case of accident or other emergency. These services are important for ensuring efficient nationwide operation of electric power systems and stable supply.
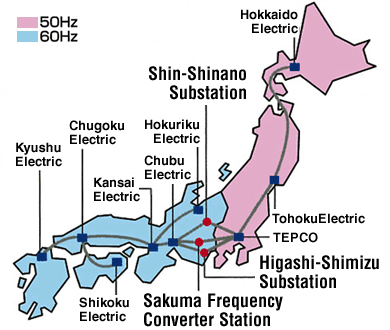
Frequencies in East and West Japan
















