Smart Meter Project
Smart Meter Project
TEPCO implemented a project to install approximately 28.4 million smart meters in all households and businesses, except for some locations where meter replacement was impossible, by the end of FY2020. These smart meters send and process power consumption (cumulative value) data every 30 minutes. We are currently working on ensuring stable operation of this smart meter system.

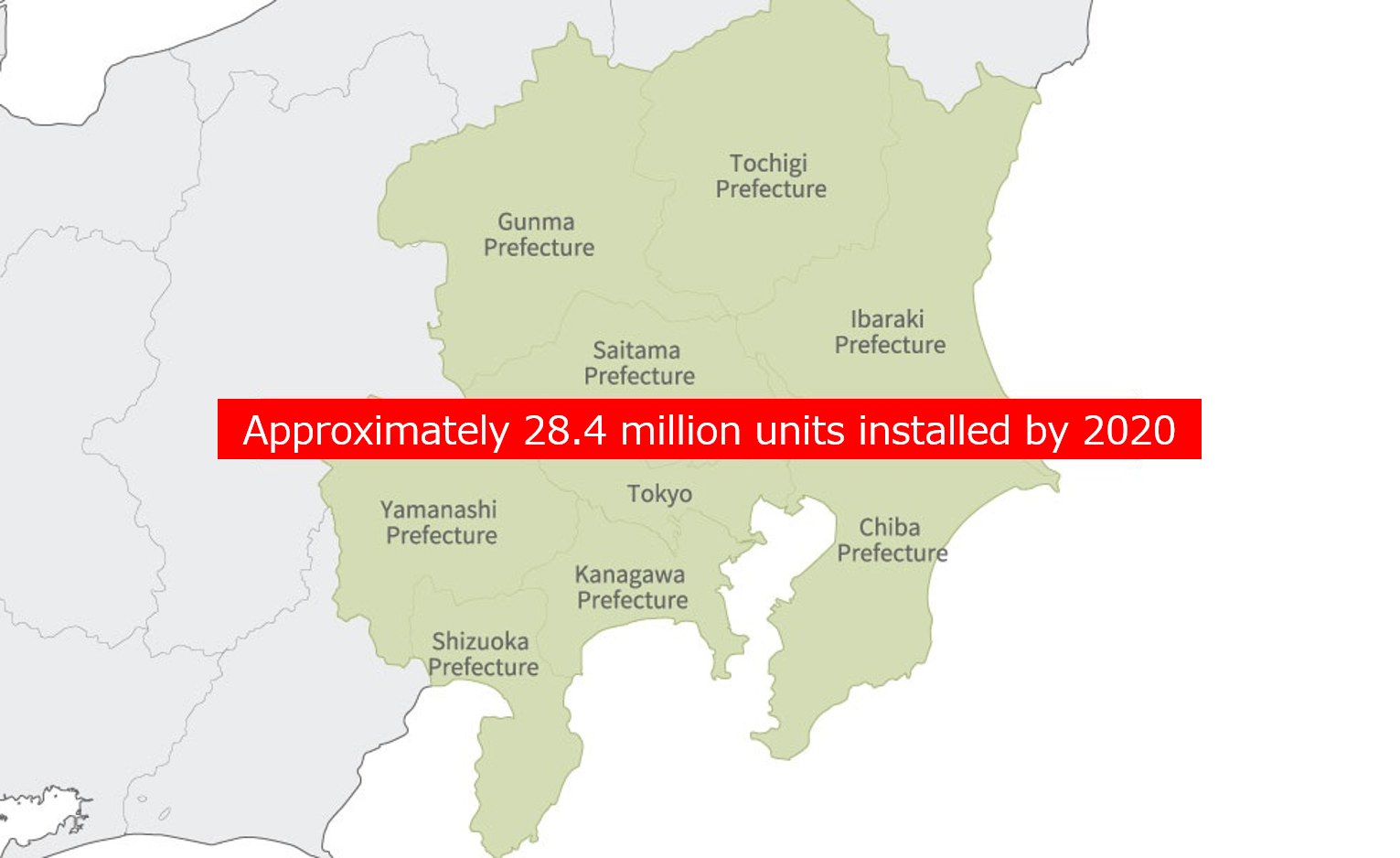
The Smart Meter System
Development of the smart meter system is divided into three main areas: (1) development of meters, (2) construction of the communication system, and (3) construction of the MDMS system. The development encompasses a wide range of large-scale tasks, from smart meter development to communication system and operational management system construction, as well as tasks to ensure the stable operation of these systems.
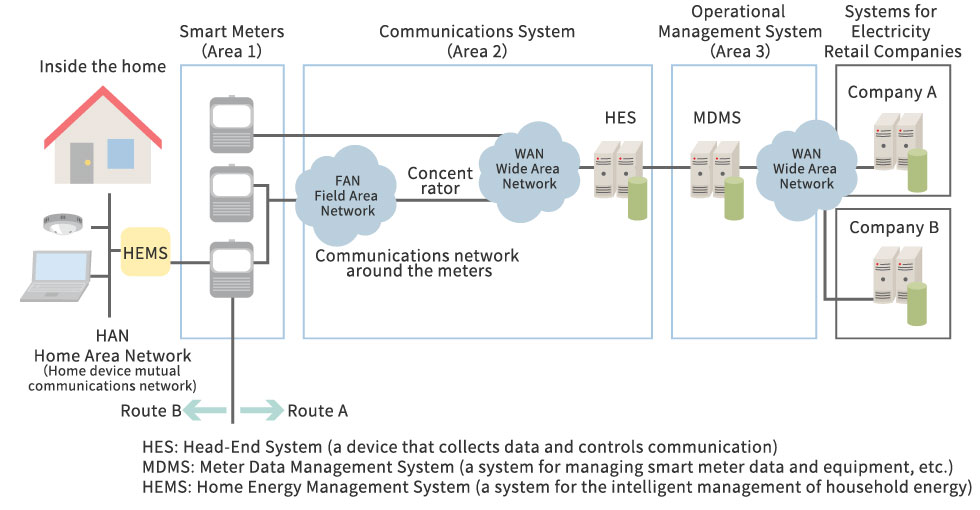
The Smart Meter Mechanism
Smart meters have a modular design with the metering unit separated from the electrical terminals. This makes it easy to safely replace the instrumentation without the need to handle live wires. In addition, since they are equipped with bidirectional metering functionality as standard, it is unnecessary to install a separate meter for cases such as when customers generate power through solar panels that is purchased by the provider.

Introduction of the Most Suitable Communication Method
Smart meters can use two communication methods such as the RF mesh network and the cellular network. Combining the most suitable method for each particular case enables a high area coverage rate and fast expansion into new areas.
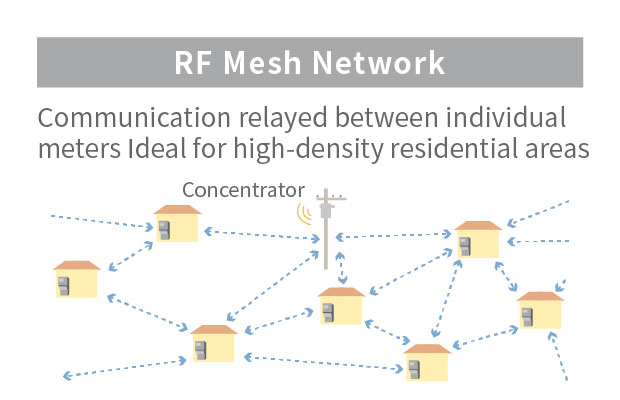
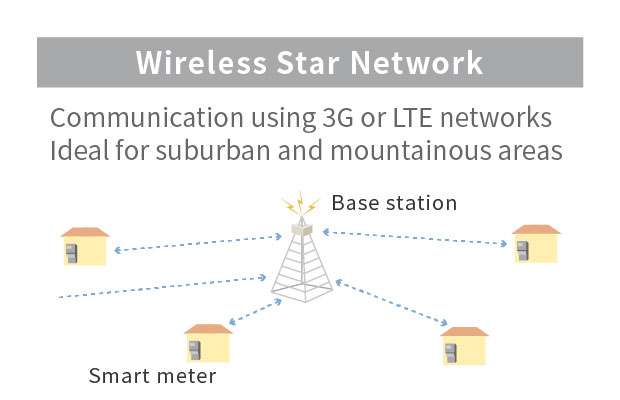
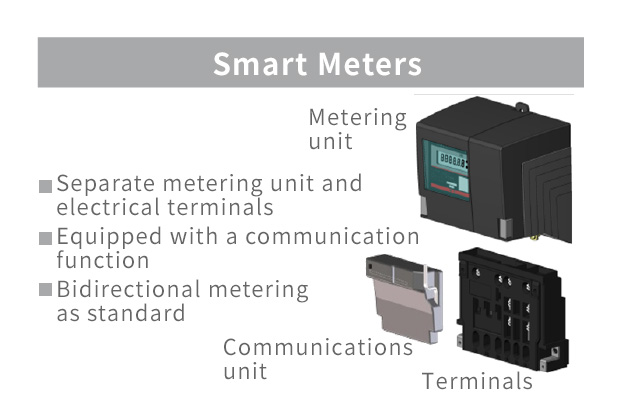
Smart Meter Communication Method: Features of the RF Mesh Method
With the RF mesh method, adjacent smart meters communicate with each other and the signal is relayed through the network to a concentrator. The use of specified low power radio signals means that wireless base stations are not necessary. As this type of network extends the range of communication of each concentrator, it is possible to create efficient facilities that can utilize multiple communication paths.
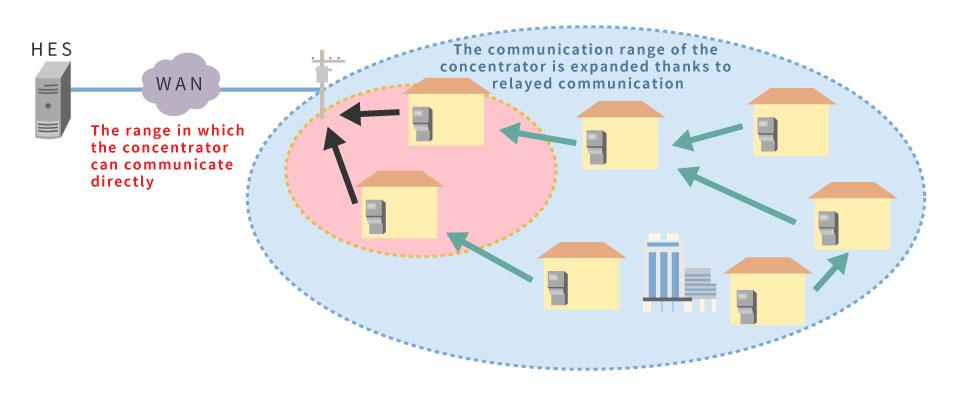
Smart Meter System Monitoring and Management
In order to centrally manage the security, operation, and maintenance of the smart meter system, we established the Smart Meter Operations Center in July 2015 for continuous monitoring and operation of the system.
Since April 2018, our Cyber Security Center has been responsible for managing the security of the smart meter system.
<Smart Meter Operations Center>
- Total system management:
Smart meter development plan progress management and network quality control. - Integrated processing center:
Opening of communications facilities and application of the corresponding electricity meter information transmission service (route B).
<Cyber Security Center>
- Security management:
Centralized management and monitoring of security for the entire smart meter system, first response when an abnormality is detected.
Key Points Upon Introduction of Smart Meters
Through the introduction of smart meters, we have considered the following key points in order to realize benefits to society, customers, and our company.
- Make maximum use of external expertise and the existing infrastructure of other business operators to suppress capital investment.
- Publish open specifications that make it easier for domestic and foreign businesses to enter the market. Promoting competition can lower costs.
- Rather than only pursuing economic rationality, make the smart meter network a system with technical expandability as social infrastructure, which will realize Demand Response and become the basis for future services that utilize meter reading data that is marked for future development.
Benefits of the Introduction of Smart Meters (1)
Smart meters are equipped with the electricity meter information transmission service (route B). This makes it possible to transmit the smart meter’s measured value to the HEMS controller* in real time. Being able to visualize the amount of electricity used based on the information received from the smart meter is expected to allow more efficient energy-saving performance. For example, the customer can allow the HEMS controller to limit the use of home appliances in periods when there are higher levels of electricity consumption.
* The HEMS controller must be prepared by the customer.
Benefits of the Introduction of Smart Meters (2)
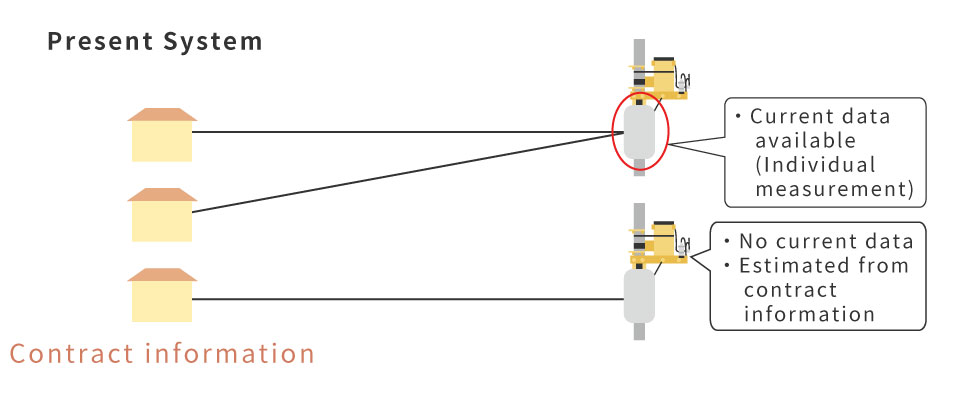
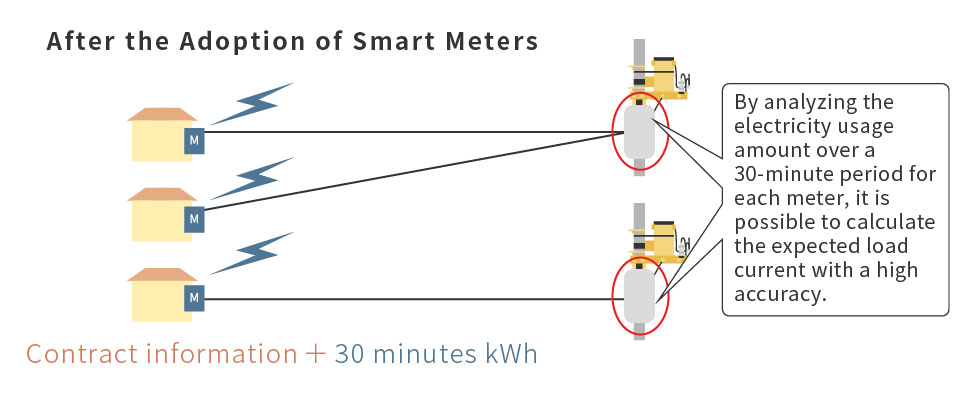
Under the current system, facilities are constructed after estimating the load current for each transformer based on customers’ contract information (contracted capacity and type). The validity of coefficients used for calculating the estimated load current is confirmed by comparing it with current data from a sample transformer. The introduction of smart meters makes it possible to understand the amount of current by analyzing the electricity usage amount over a 30-minute period for each meter. Therefore, it is possible to calculate the expected load current with a higher accuracy than the current system. This is expected to improve the efficiency of facilities thanks to being able to select more appropriate transformer capacities.
Benefits of the Introduction of Smart Meters (3)
Automated remote operation of smart meters improves the efficiency of work such as meter reading and reduces customer burden by not requiring them to be present during the reading.
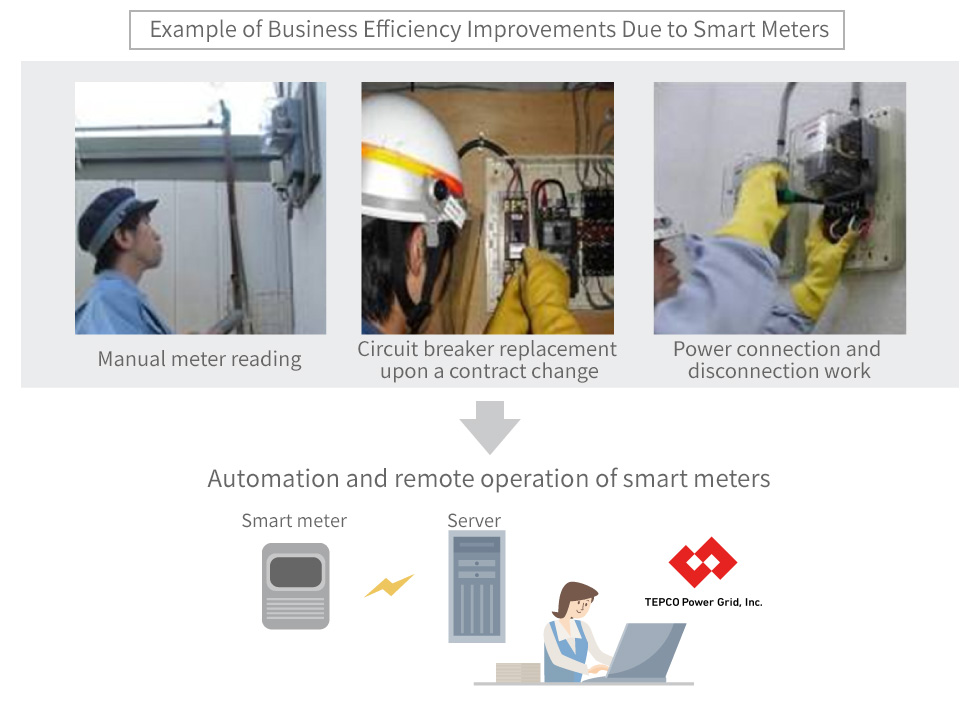
We will continue to strive to ensure stable and secure operation of the smart meter system and steadily advance the smart meter project so that we can provide services that utilize the advanced functionality of smart meters to all customers.










