Responding to
New Regulatory Requirements Compliance Reviews
at Units 6 and 7 of
the Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Station
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

Responding to New Regulatory Requirements Compliance Reviews
On September 27, 2013, TEPCO Holdings applied to the Nuclear Regulation Authority to check whether Units 6 and 7 of the Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Station comply with the New Regulatory Requirements.
This web page explains the progress of the New Regulatory Requirements Compliance Review.
We carried out 150 review meetings, 6 field surveys, and all review items for “Changes in Reactor Installation” were already discussed.
Subsequently, we will reflect properly previous observations and discussions to prepare the application for Changes in Reactor Installation.
Separate review item documents are available in Japanese. Click here.
The flow of review and inspection for checking conformity to New Regulatory Requirements. Click here.
As of August 9 , 2017
Response to terrorist attacks
- 1Response to intentional plane crashes*1

*1 Separate reviews will be conducted for specific major accident response facilities.
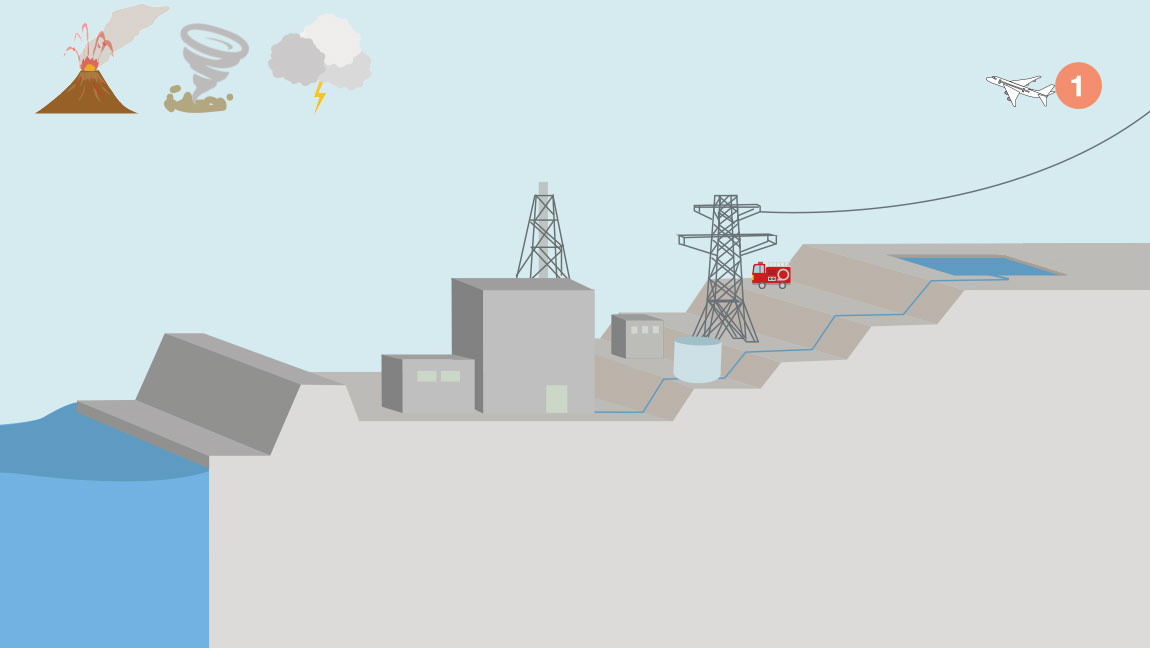
Major accident response facilities(response to major accidents)
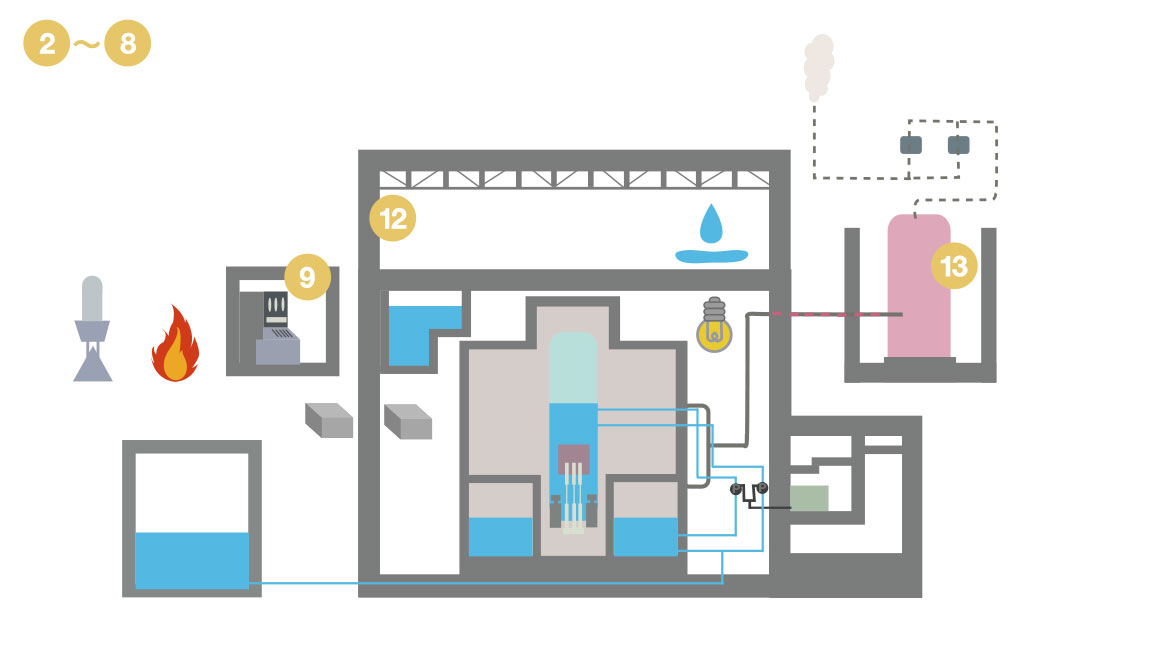
- 2Probabilistic risk assessments

- 3Selecting accident sequences

- 4Effectiveness assessments(Reactor core damage prevention measures)

- 5Effectiveness assessments(Primary containment vessel damage prevention measures)

- 6Effectiveness assessments(Fuel damage prevention measures in the spent fuel storage pools)

- 7Effectiveness assessments(Fuel damage prevention measures during reactor shutdowns)

- 8Analysis codes

- 9Reactor control room

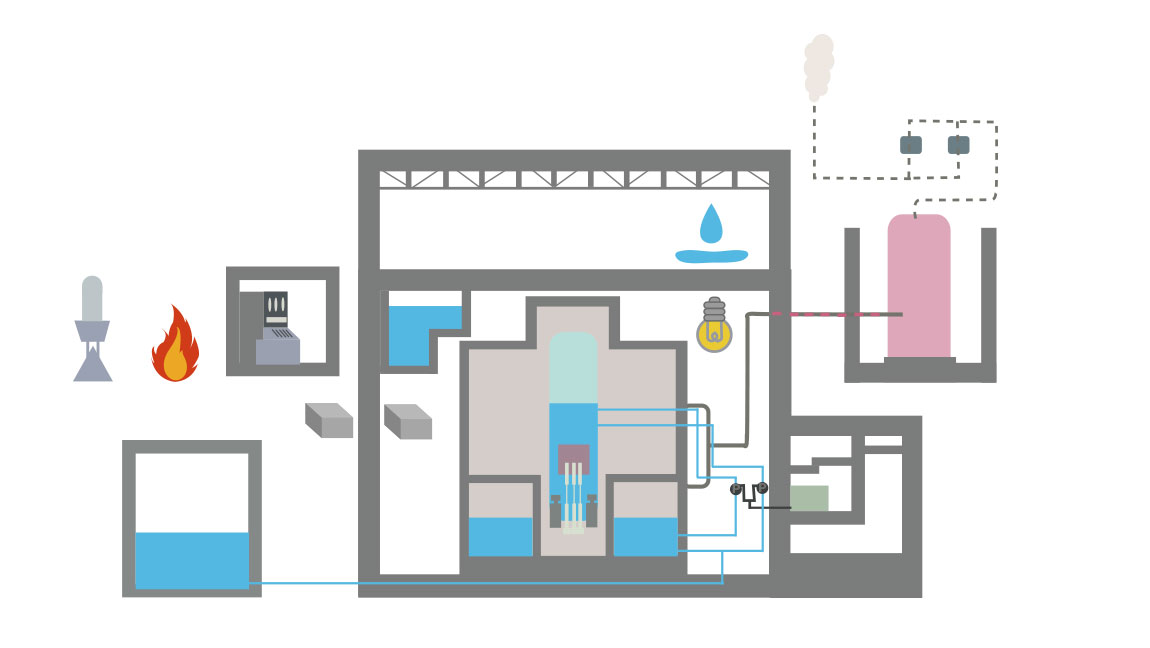
- 10Emergency response center

- 11Access routes

- 12Measures for hydrogen generation in the reactor buildings

- 13Filter vents

- 14Technical competence for major accidents

Design basis target facilities(prevention of major accidents)
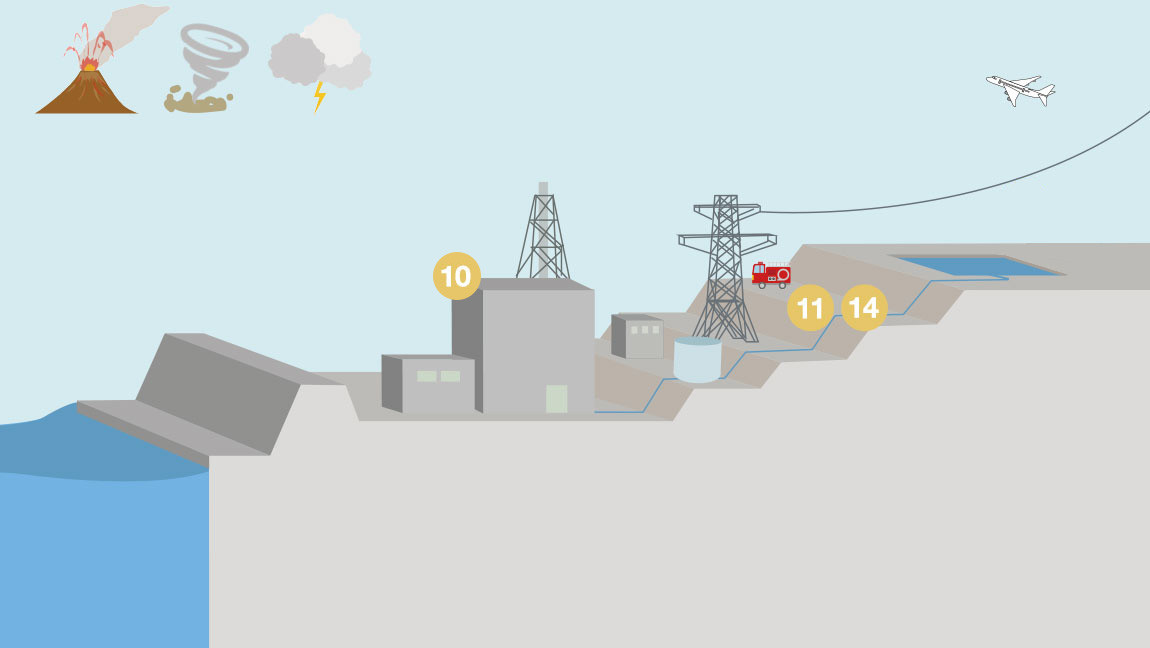
- 15Impact assessments of external fires and countermeasures

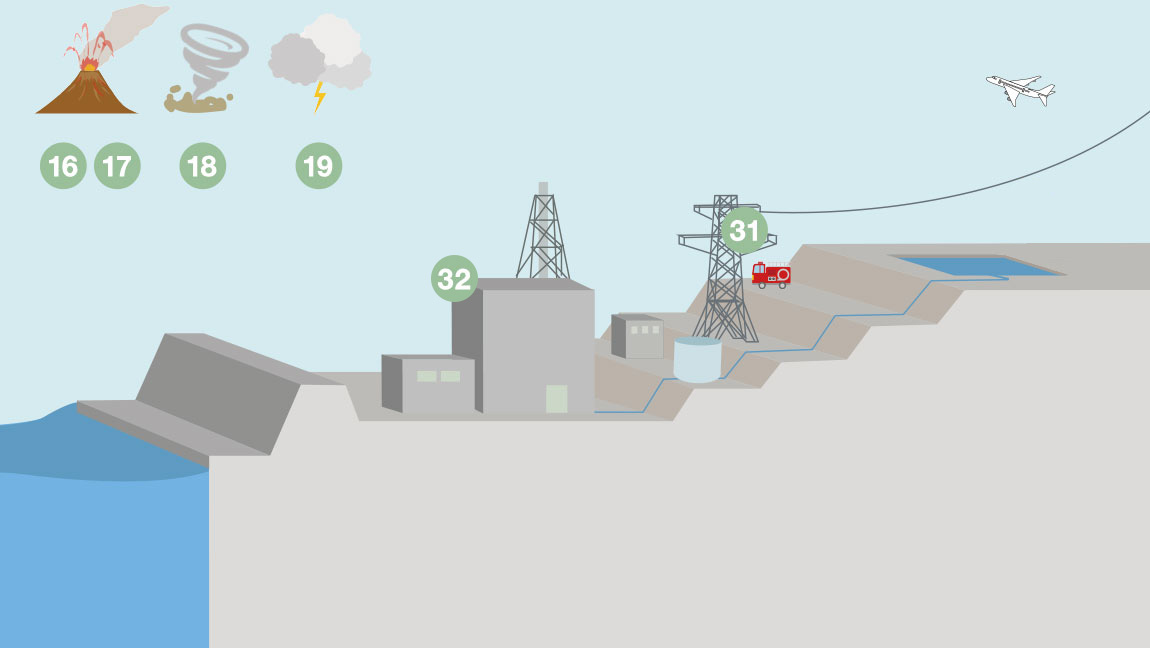
- 16Selecting target volcanoes

- 17Measures for volcanoes

- 18Impact assessments of tornadoes and countermeasures

- 19Impact assessments of other natural phenomena and countermeasures

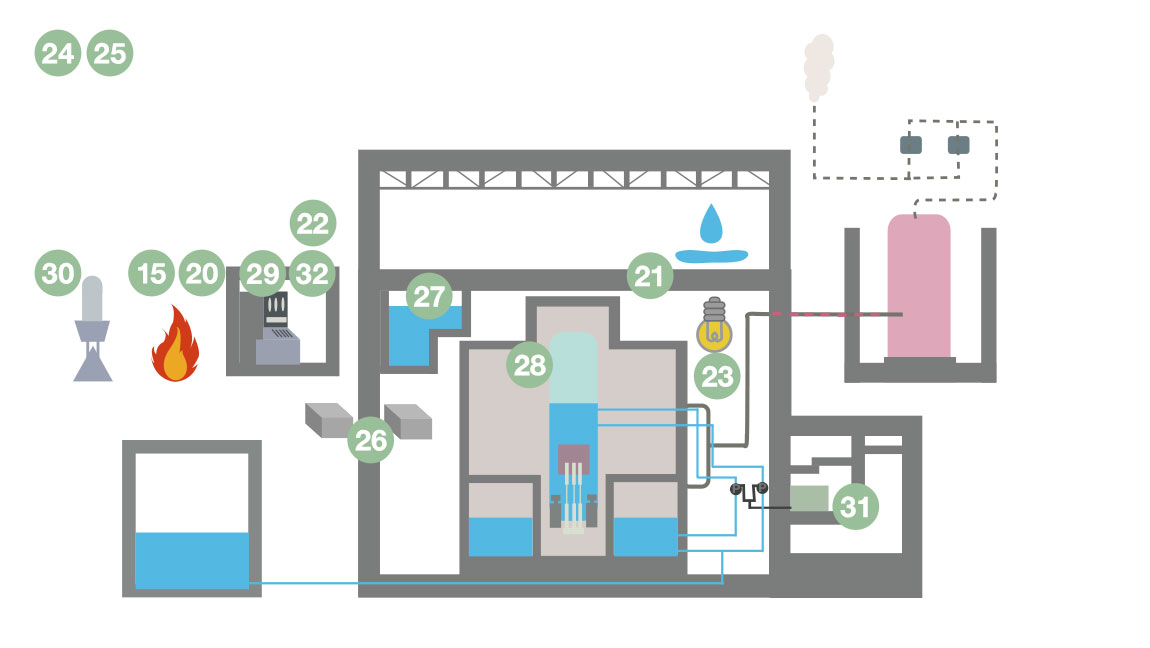
- 20Fire protection measures

- 21Measures for internal flooding

- 22Prevention of erroneous operations

- 23Evacuation passages for safety

- 24Single failure of static equipment

- 25Sharing of safety systems

- 26Countermeasure facilities for station blackouts

- 27Fuel assemblies handling and storage facilities

- 28Reactor coolant pressure boundaries*2

- 29Protection circuits for safety

- 30Monitoring and measuring devices

- 31Power-supply facilities for safety

- 32Telecommunication equipment

*2 The boundaries define the areas where equipment such as pipes reaches the same pressure level as pressure vessels during normal operations.
Response to earthquakes
and tsunamis
- 33Fault activities around the power station

- 34Fault activities within the power station

- 35Seismic motion

- 36Seismic-resistant design

- 37Stability of ground and slope

- 38Tsunami

- 39Tsunami-resistant design

- Reviewed :
- Comprehensive documents are being prepared reflecting
responses to review findings (reviewed items under
“response to earthquakes and tsunamis” completed and
explained to the Nuclear Regulation Authority).

-
Response to intentional plane crashes*1
Requirement: Procedures and equipment necessary in the event of terrorism should be prepared.
*1 Separate reviews will be conducted for specific major accident response facilities.
-
Emergency response center
Requirement: An emergency response center should be established to respond to major accidents.
-
Access routes
Requirement: Portable equipment should be deployed at locations away from the reactor buildings and can be moved to where it is necessary at the time of major accidents.
-
Technical competence for major accidents
Requirement: Procedures and equipment necessary for major accidents should be prepared.
-
Probabilistic risk assessments
Selecting accident sequences
Effectiveness assessments
Analysis codes
Requirement: Assessments should be conducted to confirm that major accident countermeasures can prevent damage to reactor cores or primary containment vessels.
-
事故シーケンス選定
重大事故対策により炉心の損傷や格納容器の破損が
防止できることを評価すること。 -
有効性評価(炉心損傷防止対策)
重大事故対策により炉心の損傷や格納容器の破損が
防止できることを評価すること。 -
有効性評価(格納容器破損防止対策)
重大事故対策により炉心の損傷や格納容器の破損が
防止できることを評価すること。 -
有効性評価
(使用済燃料貯蔵槽内の燃料損傷防止対策)重大事故対策により炉心の損傷や格納容器の破損が
防止できることを評価すること。 -
有効性評価
(運転停止中原子炉における燃料損傷防止対策)重大事故対策により炉心の損傷や格納容器の破損が
防止できることを評価すること。 -
解析コード
重大事故対策により炉心の損傷や格納容器の破損が
防止できることを評価すること。 -
Reactor control room
Requirement: Operators should be able to stay in the main control room at the time of major accidents.
-
Measures for hydrogen generation in the reactor buildings
Requirement: Equipment that prevents hydrogen explosions in the reactor buildings should be installed.
-
Filter vents
Requirement: Equipment that prevents damage to primary containment vessel should be installed.
-
Selecting target volcanoes
Requirement: Volcanoes or volcanic events should be selected and their impacts should be assessed.
-
Measures for volcanoes
Requirement: Safety functions should not be impaired by the impact of volcanoes.
-
Impact assessments of tornadoes and countermeasures
Requirement: Safety functions should not be impaired by the impact of tornadoes.
-
Impact assessments of other natural phenomena and countermeasures
Requirement: Safety functions should not be impaired by the impact of assumed natural phenomena.
-
Power-supply facilities for safety
Requirement: Electrical circuits to receive electricity from external sources and emergency power sources should be set up.
-
Telecommunication equipment
Requirement: A variety of telecommunication equipment should be installed to be used at the time of accidents.
-
Impact assessments of external fires and countermeasures
Requirement: Safety functions should not be impaired by fires or blasts occurring outside of the power station.
-
Fire protection measures
Requirement: Safety functions should not be impaired by fires within the power station.
-
Measures for internal flooding
Requirement: Safety functions should not be impaired by flooding within the reactor buildings.
-
Prevention of erroneous operations
Requirement: Facilities should be designed for easy operations to minimize the potential for human error.
-
Evacuation passages for safety
Requirement: Evacuation passages during station blackouts should be secured.
-
Single failure of static equipment
Requirement: Systems should maintain safety functions even if pipes fail for example.
-
Sharing of safety systems
Requirement: Safety systems should not be shared by multiple reactor facilities.
-
Countermeasure facilities for station blackouts
Requirement: Power supply to operate safety systems should be secured during station blackouts.
-
Fuel assemblies handling and storage facilities
Requirement: Fuel assemblies stored in the pools should be protected from any damage.
-
Reactor coolant pressure boundaries*2
Requirement: Boundaries should be set to prevent leakage of reactor coolant.
*2 The boundaries define the areas where equipment such as pipes reaches the same pressure level as pressure vessels during normal operations. -
Protection circuits for safety
Requirement: Activation of safety protection circuits should stop reactors.
-
Monitoring and measuring devices
Requirement: Radiation monitoring and measurements should be conducted even at the time of accidents.
-
Power-supply facilities for safety
Requirement: Electrical circuits to receive electricity from external sources and emergency power sources should be set up.
-
Telecommunication equipment
Requirement: A variety of telecommunication equipment should be installed to be used at the time of accidents.

-
Fault activities around the power station
Requirement: Fault activities around the power station should be assessed.
-
Fault activities within the power station
Requirement: Fault activities inside the power station should be assessed.
-
Seismic motion
Requirement: An assumed maximum seismic motion should be established as a design basis.
-
Seismic-resistant design
Requirement: Safety functions that can tolerate design basis seismic motion, should be secured.
-
Stability of ground and slope
Requirement: Ground foundation and slopes around the reactor buildings should be stable.
-
Tsunami
Requirement: An assumed maximum tsunami should be established as a design basis.
-
Tsunami-resistant design
Requirement: Safety functions that can tolerate design basis tsunami, should be secured.