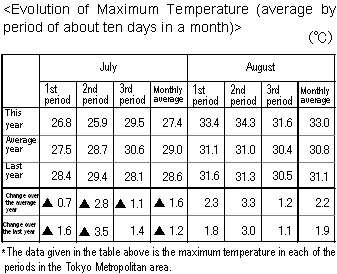
1. Meteorological Conditions and Features for This Summer Season (July and August)
-In July, the seasonal rain ("Baiu") front stayed on the south coast of Kanto region so
that there were generally many rainy and cloudy days. In addition, the end of the rainy
season was later by 12 days than in the average year (around August 1 this year and July
20 in the average year). The atmospheric temperature level was generally lower this summer
than in the average season.
-In August, the Pacific high barometric pressure overlay the Japanese territory so that it
was fair and hot in many consecutive days. The temperature level was significantly higher
in this August than in the average August. For example, a number of "very hot days" when
the maximum temperature exceeded 35oC were recorded mainly in the middle period
of August.
-In the Tokyo Metropolitan area, the monthly average maximum temperature was 33.0oC in
August and it was the fourth highest level since the meteorological observation started
in 1876. [The maximum temperature in the past was 33.7oC in August 1995.]
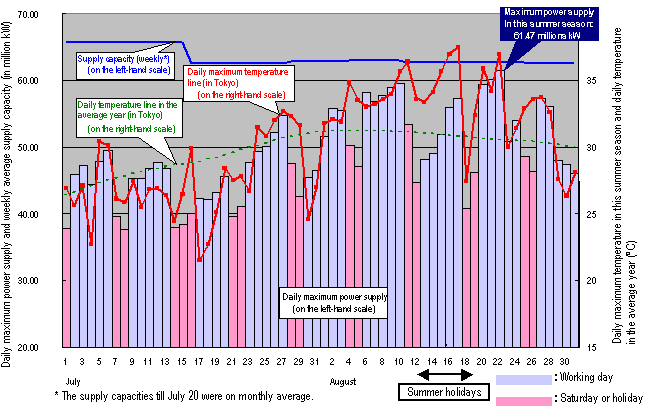
2. Evolutions of Daily Maximum Atmospheric Temperature and Maximum Power Supply in This
Summer Season
 |
 |
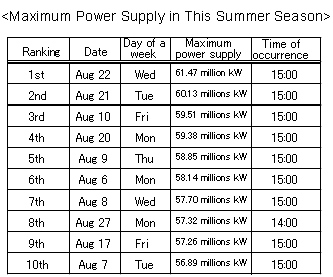 |
3. Occurrence of Maximum Power Supply in This Summer Season
-The maximum power supply in this summer season was 61.47 millions kW, which occurred
at 15:00 on August 22 (Wednesday) when the maximum atmospheric temperature of 37.0oC
in this summer season except all the holidays including the summer holidays was recorded
(in the Tokyo Metropolitan area).
-The maximum power supply in this summer season was higher by 3.14 millions kW than that
in the same season of the last year (58.06 millions kW on July 14, 2006)
<Temporary emergency measures taken to meet the excessive demand>
Shiobara Power Station (0.90 millions kW) had been administratively punished by the
withdrawal of its water use permit for the reason of its illegal water intake. However,
the plant was allowed to receive the water use permit as the temporary emergency action
(for the period of July 30 to September 7).
<Reference>
The maximum supply of electric power in this summer season (61.47 millions kW on August 22)
did not exceed that of the past (64.3 millions kW on July 24, 2001), probably due to the
following factors:
(1) The public contributed to saving their consumption of power;
(2) The bypassed demand was higher than that in fiscal year 2001;
(3) The maximum temperature on the day when the maximum power supply was recorded this
summer was lower than that on the day of the maximum power supply in the past.
|